The original Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre press release can be read here.
In a new study, researchers from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) and the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Argonne National Laboratory have teamed up to capture neon within a porous crystalline framework. Neon is well known for being the most unreactive element and is a key component in semiconductor manufacturing, but this is the first time neon has ever been studied within an organic or metal-organic framework. The results, which include critical studies at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility at Argonne, also point the way towards a more economical and greener industrial process for neon production.
Neon is an element that is well-known to the general population due to its iconic use in neon signs, especially in city centres in the United States from the 1920s to the 1960s. In recent years, the industrial use of neon has become dominated by use in excimer lasers to produce semiconductors. Despite being the fifth most abundant element in the atmosphere, the cost of pure neon gas has risen significantly over the years, increasing the demand for better ways to separate and isolate the gas.
During 2015, CCDC scientists presented a talk at the annual American Crystallographic Association (ACA) meeting on the array of elements that have been studied within an organic or metal-organic environment, challenging the crystallographic community to find the next and possibly last element to be added to the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD). A chance encounter at that meeting with Andrey Yakovenko, a beamline scientist at the APS, resulted in a collaborative project to capture neon – the 95th element to be observed in the CSD.
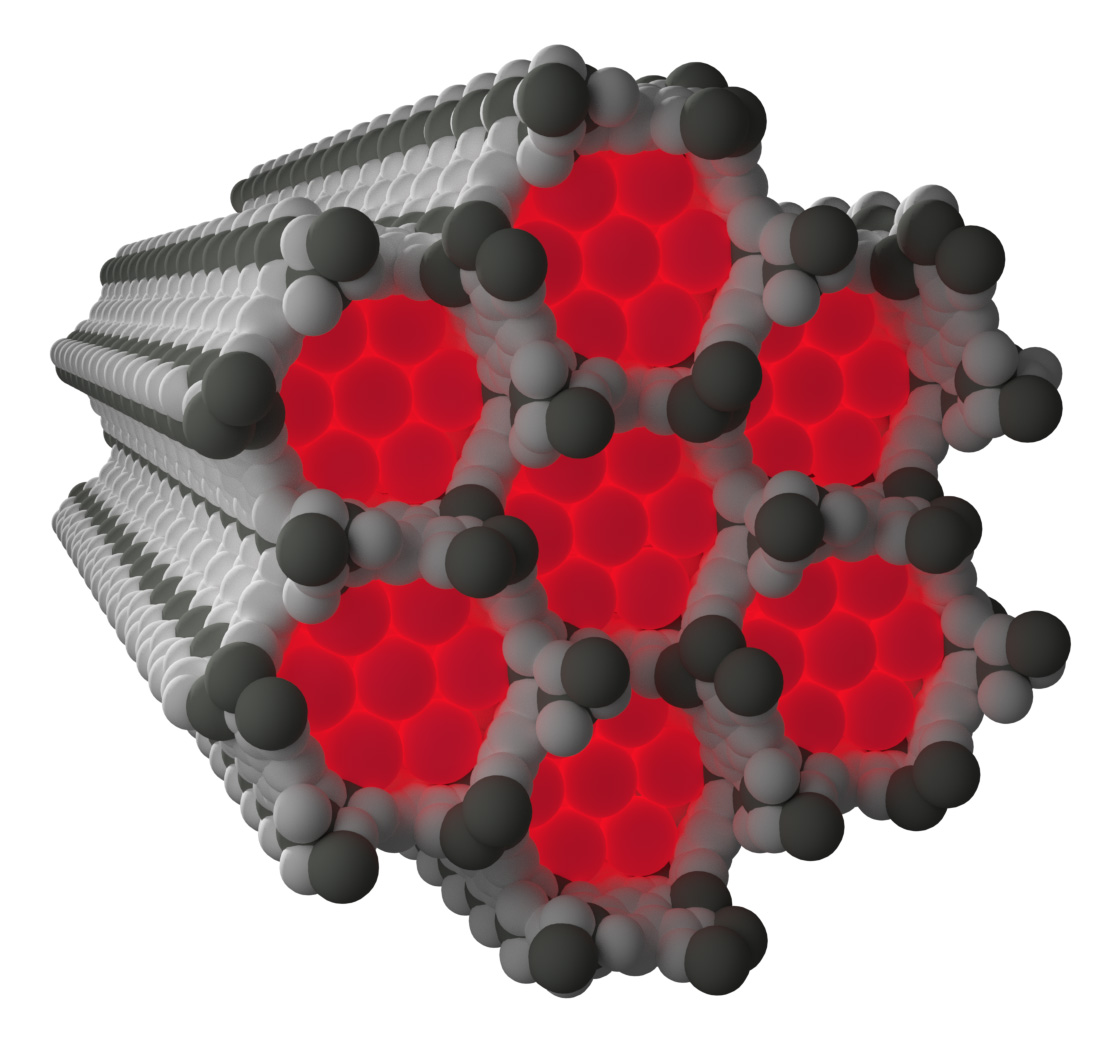
Neon’s low reactivity, along with the weak scattering of x-rays due to its relatively low number of electrons, means that conclusive experimental observation of neon captured within a crystalline framework is very challenging. In situ high-pressure gas flow experiments performed at X-ray Science Division beamline 17-BM at the APS using the x-ray powder diffraction technique at low temperatures managed to elucidate the structure of two different metal-organic frameworks with neon gas captured within the frameworks.
“This is a really exciting moment representing the latest new element to be added to the CSD and quite possibly the last given the experimental and safety challenges associated with the other elements yet to be studied” said Peter Wood, Senior Research Scientist at CCDC and lead author on the paper published in Chemical Communications. “More importantly, the structures reported here show the first observation of a genuine interaction between neon and a transition metal suggesting the potential for future design of selective neon capture frameworks”
The structure of neon captured within the framework known as NiMOF-74, a porous framework built from nickel metal centres and organic linkers, shows clear nickel to neon interactions forming at low temperatures significantly shorter than you would expect from a typical weak contact.
Andrey Yakovenko said “These fascinating results show the great capabilities of the scientific program at 17-BM and the Advanced Photon Source. Previously, we have been doing experiments at our beamline using other much heavier, and therefore easily detectable, noble gases such as xenon and krypton. However, after meeting co-authors Pete, Colin, Amy, and Suzanna at the ACA meeting, we decided to perform these much more complicated experiments using the very light and inert gas - neon. In fact, only by using a combination of in situ x-ray powder diffraction measurements, low temperature, and high pressure have we been able to conclusively identify the neon atom positions beyond reasonable doubt.”
Summarising the findings, Chris Cahill, Past President of the ACA and Professor of Chemistry at George Washington University, said “This is a really elegant piece of in situ crystallography research and it is particularly pleasing to see the collaboration coming about through discussions at an annual ACA meeting”.
See: Peter A. Wood1*, Amy A. Sarjeant1, Andrey A. Yakovenko2, Suzanna C. Ward1, and Colin R. Groom1, “Capturing neon – the first experimental structure of neon trapped within a metal–organic environment,” Chem. Commun. 52, 10048 (2016). DOI: 10.1039/c6cc04808k
Author affiliations: 1Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, 2Argonne National Laboratory
Correspondence: *[email protected]
A.A.Y. thanks the Director’s Postdoctoral Fellowship program at Argonne. Other costs were met from the CCDC scholarship and outreach fund. This research used resources of the APS, a DOE Office of Science user facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under contract no. DE-AC02- 06CH11357.
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation's first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America's scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit the Office of Science website.